Topics
| SL. No. | Name | Links | Youtube Link | G Drive | Category | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | How can i ask question on forum? |
Dear Friends Please let us know how can i ask question and reply on forum. |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | Big Data in Rail Freight sector of Indian Railways |
The concept of Big Data is at the forefront of new technology in rail freight sector. Analytics based on Big Data is a new field in the transportation sector which presents challenges to implement & the opportunities to gain from the Big Data based analytics in terms of better preventive & predictive Asset maintenance activities. The Indian Railways has been in the last ten years implemented various condition monitoring mechanisms for its fleet of Freight wagons like Wheel Impact Load Detector (WILD), Hot Box Detector (HBD), Online Monitoring of Rolling Stock (OMRS) & RFID tags for wagons. All these packages will help to improve the service availability & enhanced maintenance periodicity. Mostly the data generated is used to give maintenance alerts. Data is also generated at the maintenance points while the maintenance is being undertaken & periodic checking at the en route stations. Most of this data is now available in digital form & can be utilized for gaining predictive insights. Big Data can be defined as data so huge which is beyond the normal computing capacity available. The volume can be several GBs per day. Big data can be characterized by several attributes called as the Vs of Big Data : Volume, Variety, Veracity, Valence , Velocity & Value. A basic Big Data model works towards acquiring, pre processing, analyzing & getting insights from the various streams of data which is being generated by various sources- Machines, People & Organizations in the ambit of Indian Railways. Each of this step is a major step involving various iterations with a single objective of getting Actionable Insights from the torrents of data. These insights will be valuable for the Indian Railways in achieving high standards of serviceability, key decisions related to the sufficiency of new technology, increasing the modal share, optimization of the available infrastructure for freight maintenance & prepare a course of action for the heavy haul traffic. |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
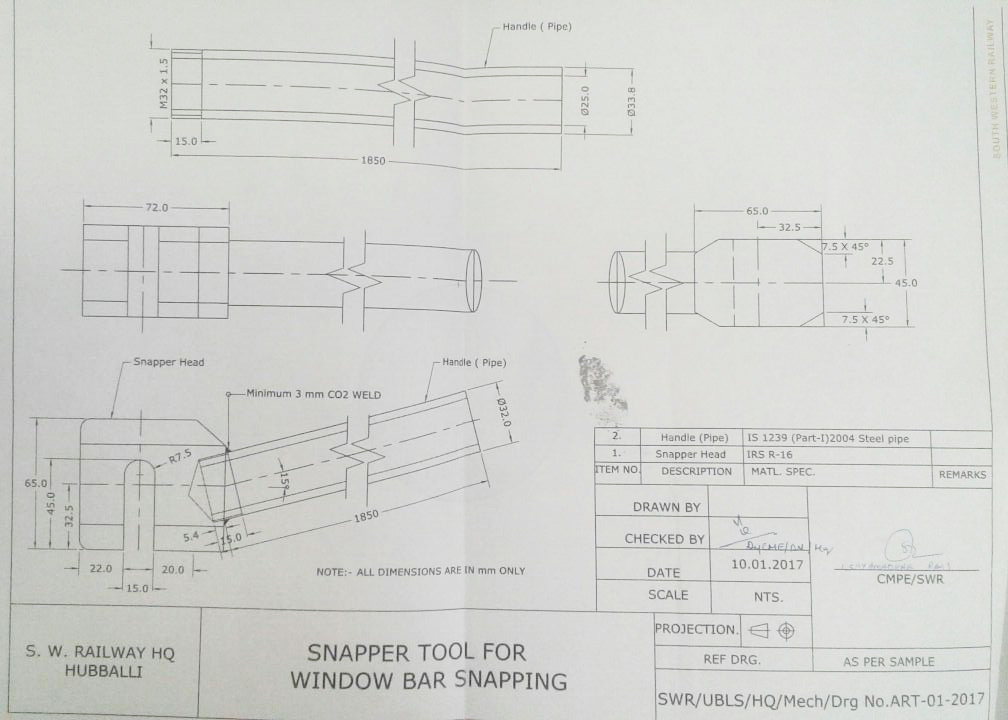
| 43 | Window bar snapper tool developed at UBL depot |
Hubli Division of South Western railways has developed a very effective Rescue Device i.e. Manually operated Coach Window rod Snapper Tool for removing window rods quickly which helps in evaculating passengeres from coach at Accident Sites quickly
|
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | Bio toilet working models have been displayed at Hubli |
Bio toilet working models have been displayed at Hubli & VSG Railway station. The advantages and the working system of Bio toilets has been displayed on Eco solvent vinyl boards in vernacular language for awareness of passenger. UBL
VSG
|
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | Silent block extracting tool |
To press the anchor link silent block, a gadget has been fabricated, which is very easy to install & consumption of manpower is very less. The gadget is made of one rectangular frame/stand with base plate fixed at the centre for anchor link resting & one top plate (floating) for pressing the silent block. The top plate hangs with springs on either ends with sufficient gap between the base plate & top plate for easy placing of anchor link & silent block. Further, the top plate to be pressed in downward direction with the help of hydraulic jack for pressing the silent block in anchor link eye. Once the work is done, hydraulic jack to be released & it will move upward along with top plate automatically since, the spring tension get release & goes to its normal position.
|
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 46 | Bio toilet cleaning tool |
Bio toilet cleaning tool has been developed by UBL Division to clear the scales formed in commode pan neck area. The scales and muck accumulated in this area is the main cause for foul smell in bio toilets. Till now about 75% of the coaches of UBL Division have been covered and the results are satisfactory. |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | Gadget for lifting of side buffers for fitment in coaches |
Name of the Gadget: Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gw54o-vMNr4
Rectangular shaped Gadget Description:
This rectangular shaped (120”x 14.5”) gadget (shown in picture below) is made up of SS pipes of 28 mm OD,1.5 mm thick with Sliding Table arrangement. This table is provided in such a way that the table with buffer can move freely on the longitudinal pipes of the gadget. There is a fixing arrangement at the ends of ‘A’ to be fixed with the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Handles at the end ‘B’ have been provided for easy lifting of gadget manually. The gadget works as a Class 2 lever with fulcrum at end ‘A’ i.e. the head stock, effort at end ‘B’ and load (buffer) in between to achieve maximum Mechanical Advantage. Thus the gadget works successfully with less man power, time and ensuring safety.
Use of the Gadget:
i) Fitment of soft buffer in ICF designed CBC fitted coaches
ii) Replacement of buffer in conventional coaches
Requirements for fitment of buffer:
i) Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches developed at SRC
ii) Box Spanner, Size 36
iii) Manpower-3 persons to be provided
iv) Wooden Skids- 4 nos.
Procedure for fitment of buffer:
Before fitment of buffer in a coach, ensure protection of lines and provide skids on the lines to avoid rolling of wheels of the coach. Steps for fitment of buffer are mentioned as under:
Benefit: I) The gadget is simple and portable. |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | Gadget for lifting of side buffers for fitment in coaches |
Name of the Gadget: Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gw54o-vMNr4
Rectangular shaped Gadget Description:
This rectangular shaped (120”x 14.5”) gadget (shown in picture below) is made up of SS pipes of 28 mm OD,1.5 mm thick with Sliding Table arrangement. This table is provided in such a way that the table with buffer can move freely on the longitudinal pipes of the gadget. There is a fixing arrangement at the ends of ‘A’ to be fixed with the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Handles at the end ‘B’ have been provided for easy lifting of gadget manually. The gadget works as a Class 2 lever with fulcrum at end ‘A’ i.e. the head stock, effort at end ‘B’ and load (buffer) in between to achieve maximum Mechanical Advantage. Thus the gadget works successfully with less man power, time and ensuring safety.
Use of the Gadget:
i) Fitment of soft buffer in ICF designed CBC fitted coaches ii) Replacement of buffer in conventional coaches
Requirements for fitment of buffer:
i) Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches developed at SRC ii) Box Spanner, Size 36 iii) Manpower-3 persons to be provided iv) Wooden Skids- 4 nos.
Procedure for fitment of buffer:
Before fitment of buffer in a coach, ensure protection of lines and provide skids on the lines to avoid rolling of wheels of the coach. Steps for fitment of buffer are mentioned as under:
Step-1 End ‘A’ of the gadget to be fixed on the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Step-2 Fix buffer on Sliding Table provided on the gadget Step-3 Push the table manually from end ‘B’’ to end ‘A’ Step-4 Simultaneously end ‘B’ of the Gadget is to be lifted gradually with the help of handles provided. Step-5 Place the buffer on the head stock and fix two upper Nylock nut bolts provided in the head stock to hold the buffer securely. Step-6 Release the gadget Step-7 Fix the lower two Nylock nut bolts. Ensure proper tightness of all Nylock nut bolts. Benefit: I) The gadget is simple and portable. |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | In-house Development of Heavy Duty Hydraulic Press |
It requires a hydraulic bottle jack and different types/sizes of adapters as per job and all these things have been developed in house.
Benefits:
i) Easy to work ii) Less manpower required iii) Less time required |
PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | Machine Learning – A Primer |
What is Machine Learning? Some Examples How does it work?
We feed the above images of cats and dogs to a ML program. The images are converted to matrix of pixel values, and we assign the label of “0” for a cat and “1” for a dog, as appropriate for each image. The ML program looks at the common features among images classified as “0”. Similarly, the ML program tries to identify common features among images classified as “1”. This was hitherto considered to be an exclusive attribute of animals in general and humans in particular. Cognition is a term that means using our brain to make sense of the environment. “Machines” were not expected to display cognitive behavior. Since ML is in the business of predictions, there is an element of uncertainty. No ML algorithm can claim to have perfected the art of prediction. The subjects of predictions and uncertainty are classified under the subject of probability, which itself falls under the broader subject of statistics. Thus, when analyzing a new image, the ML program compares it with the earlier images it has “seen” and assigns the “most likely” label to the new image. ML practitioners must therefore be well versed in computer programming as well as statistics. Getting the predictions right Can I learn ML? https://medium.freecodecamp.org/every-single-machine-learning-course-on-the-internet-ranked-by-your-reviews-3c4a7b8026c0
|
PDF Open |














 A heavy duty hydraulic press has been developed by Sick line, SRC coaching depot which is very much useful to insert and extract different types of bushes like control arm, traction centre, traction rod, vertical roll link of LHB coaches, centre pivot push, anchor link bush of ICF/HYBRID coaches.
A heavy duty hydraulic press has been developed by Sick line, SRC coaching depot which is very much useful to insert and extract different types of bushes like control arm, traction centre, traction rod, vertical roll link of LHB coaches, centre pivot push, anchor link bush of ICF/HYBRID coaches.
 Thus the ML program “learns” about features that are unique to cats. When fed a new unclassified image, the ML program compares the features of the new image with the ones it has learned earlier and assigns the new image a classification based on its past “training”.
Thus the ML program “learns” about features that are unique to cats. When fed a new unclassified image, the ML program compares the features of the new image with the ones it has learned earlier and assigns the new image a classification based on its past “training”.