| SL. No. | Name | Description | Course | Youtube Link | G Drive | Category | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41 | How can i ask question on forum? |
Dear Friends Please let us know how can i ask question and reply on forum. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | Big Data in Rail Freight sector of Indian Railways |
The concept of Big Data is at the forefront of new technology in rail freight sector. Analytics based on Big Data is a new field in the transportation sector which presents challenges to implement & the opportunities to gain from the Big Data based analytics in terms of better preventive & predictive Asset maintenance activities. The Indian Railways has been in the last ten years implemented various condition monitoring mechanisms for its fleet of Freight wagons like Wheel Impact Load Detector (WILD), Hot Box Detector (HBD), Online Monitoring of Rolling Stock (OMRS) & RFID tags for wagons. All these packages will help to improve the service availability & enhanced maintenance periodicity. Mostly the data generated is used to give maintenance alerts. Data is also generated at the maintenance points while the maintenance is being undertaken & periodic checking at the en route stations. Most of this data is now available in digital form & can be utilized for gaining predictive insights. Big Data can be defined as data so huge which is beyond the normal computing capacity available. The volume can be several GBs per day. Big data can be characterized by several attributes called as the Vs of Big Data : Volume, Variety, Veracity, Valence , Velocity & Value. A basic Big Data model works towards acquiring, pre processing, analyzing & getting insights from the various streams of data which is being generated by various sources- Machines, People & Organizations in the ambit of Indian Railways. Each of this step is a major step involving various iterations with a single objective of getting Actionable Insights from the torrents of data. These insights will be valuable for the Indian Railways in achieving high standards of serviceability, key decisions related to the sufficiency of new technology, increasing the modal share, optimization of the available infrastructure for freight maintenance & prepare a course of action for the heavy haul traffic. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
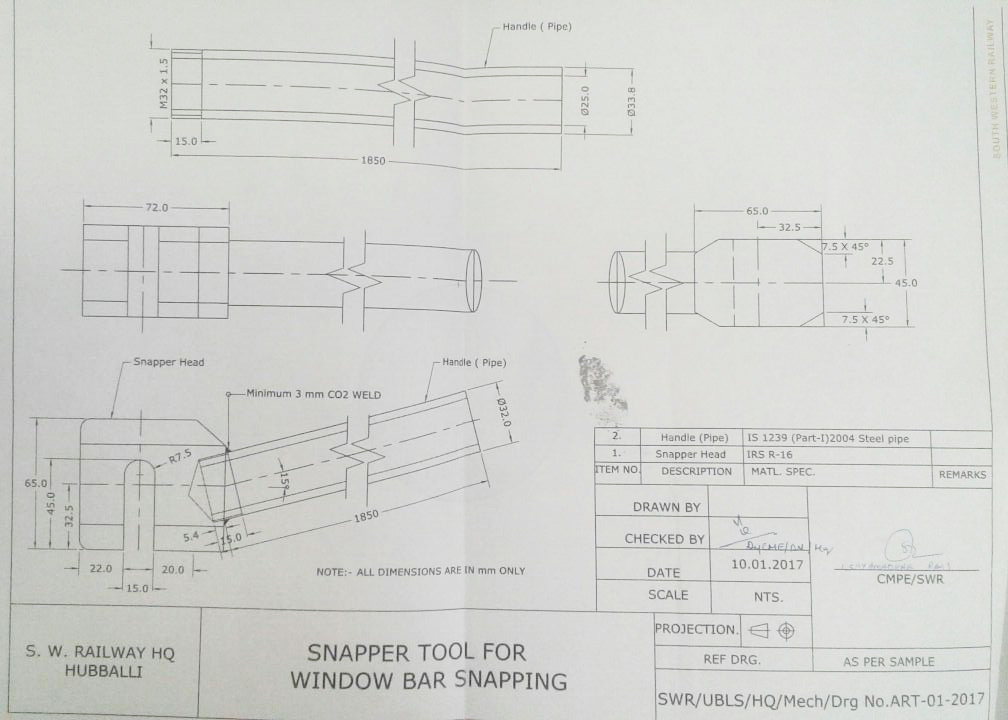
| 43 | Window bar snapper tool developed at UBL depot |
Hubli Division of South Western railways has developed a very effective Rescue Device i.e. Manually operated Coach Window rod Snapper Tool for removing window rods quickly which helps in evaculating passengeres from coach at Accident Sites quickly
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | Bio toilet working models have been displayed at Hubli |
Bio toilet working models have been displayed at Hubli & VSG Railway station. The advantages and the working system of Bio toilets has been displayed on Eco solvent vinyl boards in vernacular language for awareness of passenger. UBL
VSG
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | Silent block extracting tool |
To press the anchor link silent block, a gadget has been fabricated, which is very easy to install & consumption of manpower is very less. The gadget is made of one rectangular frame/stand with base plate fixed at the centre for anchor link resting & one top plate (floating) for pressing the silent block. The top plate hangs with springs on either ends with sufficient gap between the base plate & top plate for easy placing of anchor link & silent block. Further, the top plate to be pressed in downward direction with the help of hydraulic jack for pressing the silent block in anchor link eye. Once the work is done, hydraulic jack to be released & it will move upward along with top plate automatically since, the spring tension get release & goes to its normal position.
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 46 | Bio toilet cleaning tool |
Bio toilet cleaning tool has been developed by UBL Division to clear the scales formed in commode pan neck area. The scales and muck accumulated in this area is the main cause for foul smell in bio toilets. Till now about 75% of the coaches of UBL Division have been covered and the results are satisfactory. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | Gadget for lifting of side buffers for fitment in coaches |
Name of the Gadget: Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gw54o-vMNr4
Rectangular shaped Gadget Description:
This rectangular shaped (120”x 14.5”) gadget (shown in picture below) is made up of SS pipes of 28 mm OD,1.5 mm thick with Sliding Table arrangement. This table is provided in such a way that the table with buffer can move freely on the longitudinal pipes of the gadget. There is a fixing arrangement at the ends of ‘A’ to be fixed with the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Handles at the end ‘B’ have been provided for easy lifting of gadget manually. The gadget works as a Class 2 lever with fulcrum at end ‘A’ i.e. the head stock, effort at end ‘B’ and load (buffer) in between to achieve maximum Mechanical Advantage. Thus the gadget works successfully with less man power, time and ensuring safety.
Use of the Gadget:
i) Fitment of soft buffer in ICF designed CBC fitted coaches
ii) Replacement of buffer in conventional coaches
Requirements for fitment of buffer:
i) Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches developed at SRC
ii) Box Spanner, Size 36
iii) Manpower-3 persons to be provided
iv) Wooden Skids- 4 nos.
Procedure for fitment of buffer:
Before fitment of buffer in a coach, ensure protection of lines and provide skids on the lines to avoid rolling of wheels of the coach. Steps for fitment of buffer are mentioned as under:
Benefit: I) The gadget is simple and portable. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | Gadget for lifting of side buffers for fitment in coaches |
Name of the Gadget: Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gw54o-vMNr4
Rectangular shaped Gadget Description:
This rectangular shaped (120”x 14.5”) gadget (shown in picture below) is made up of SS pipes of 28 mm OD,1.5 mm thick with Sliding Table arrangement. This table is provided in such a way that the table with buffer can move freely on the longitudinal pipes of the gadget. There is a fixing arrangement at the ends of ‘A’ to be fixed with the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Handles at the end ‘B’ have been provided for easy lifting of gadget manually. The gadget works as a Class 2 lever with fulcrum at end ‘A’ i.e. the head stock, effort at end ‘B’ and load (buffer) in between to achieve maximum Mechanical Advantage. Thus the gadget works successfully with less man power, time and ensuring safety.
Use of the Gadget:
i) Fitment of soft buffer in ICF designed CBC fitted coaches ii) Replacement of buffer in conventional coaches
Requirements for fitment of buffer:
i) Gadget for lifting of Side Buffers for fitment in coaches developed at SRC ii) Box Spanner, Size 36 iii) Manpower-3 persons to be provided iv) Wooden Skids- 4 nos.
Procedure for fitment of buffer:
Before fitment of buffer in a coach, ensure protection of lines and provide skids on the lines to avoid rolling of wheels of the coach. Steps for fitment of buffer are mentioned as under:
Step-1 End ‘A’ of the gadget to be fixed on the bottom holes (2 nos.) on the head stock where the buffer to be fitted. Step-2 Fix buffer on Sliding Table provided on the gadget Step-3 Push the table manually from end ‘B’’ to end ‘A’ Step-4 Simultaneously end ‘B’ of the Gadget is to be lifted gradually with the help of handles provided. Step-5 Place the buffer on the head stock and fix two upper Nylock nut bolts provided in the head stock to hold the buffer securely. Step-6 Release the gadget Step-7 Fix the lower two Nylock nut bolts. Ensure proper tightness of all Nylock nut bolts. Benefit: I) The gadget is simple and portable. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | In-house Development of Heavy Duty Hydraulic Press |
It requires a hydraulic bottle jack and different types/sizes of adapters as per job and all these things have been developed in house.
Benefits:
i) Easy to work ii) Less manpower required iii) Less time required |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | Machine Learning – A Primer |
What is Machine Learning? Some Examples How does it work?
We feed the above images of cats and dogs to a ML program. The images are converted to matrix of pixel values, and we assign the label of “0” for a cat and “1” for a dog, as appropriate for each image. The ML program looks at the common features among images classified as “0”. Similarly, the ML program tries to identify common features among images classified as “1”. This was hitherto considered to be an exclusive attribute of animals in general and humans in particular. Cognition is a term that means using our brain to make sense of the environment. “Machines” were not expected to display cognitive behavior. Since ML is in the business of predictions, there is an element of uncertainty. No ML algorithm can claim to have perfected the art of prediction. The subjects of predictions and uncertainty are classified under the subject of probability, which itself falls under the broader subject of statistics. Thus, when analyzing a new image, the ML program compares it with the earlier images it has “seen” and assigns the “most likely” label to the new image. ML practitioners must therefore be well versed in computer programming as well as statistics. Getting the predictions right Can I learn ML? https://medium.freecodecamp.org/every-single-machine-learning-course-on-the-internet-ranked-by-your-reviews-3c4a7b8026c0
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 51 | Knowledge center portal at ICF |
A web portal – Knowledge Center has been hosted in Railnet website of ICF. The IP address of ICF Railnet is: 10.53.4.11 The same portal of Knowledge Center will also be hosted at http://icf.gov.in within a short time. This portal provides knowledge on the study materials on welding processes, power sources, troubles shooting of power source, Welding defects, frequently asked questions etc. Also videos, posters, photo graphs of weld cut section are also available. A discussion forum has been designed for users with ICF to post queries. AWTI faculties or anyone can post reply for the same. Brief over view of the portal is given below.
Information Description Tab on the main page Link to follow Knowledge center Knowledge Center - A web portal containing information regarding welding. Knowledge center Knowledge center Welding technology
Safety in welding. Knowledge center >Welding technology>Safety. Welding procedures for various weld joints. ISO 3834 (WPS). >Welding technology> ISO 3834>IMS>ISO 3834-2:2005> (WPS) Weld Cut section Models. >Welding technology> Cut section Models. Welding Videos. >Welding technology> Welding Videos. Booklet on welding power source Trouble shooting. >Welding technology> Trouble shooting guide Welding Improvement Projects done at ICF. >Welding technology> improvement Projects Posters showing welding processes and testing. >Welding technology> Posters Published Welding Study papers in journals by AWTI faculty members. >Welding technology> Published Welding Study papers GMAW power source Trouble shooting Videos. >Welding technology> Trouble shooting Videos Welding Hand Book containing information related to Railway applications. >Welding technology> Welding Hand Book Welding procedure Specification for MMAW welding process >Welding technology> Welding Parameter Welding power source maintenance Catalogue and information related to power sources used at ICF. Knowledge center >Welding Power Source Maintenance Hub Training calendar. AWTI 2018-19 Calendar with course contents. Knowledge center >Training calendar Training facilities Infrastructure available in workshop for training and CMT lab testing at AWTI. Knowledge center >Facilities Core group members Contact details of faculty members of AWTI. Knowledge center >Core group members Help desk To post queries regarding welding and get replies Knowledge center >Help desk FAQ Trouble shooting info on power sources Knowledge center >FAQ’s
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 52 | Direct Part Marking (DPM) – An introduction |
With DPM, parts and components are marked once with some essential information that allow for its continued track-and-trace through its lifetime. This applies to individual components and also to their assembly. The largest users of DPM technology in India is the automotive sector. From individual fasteners, to piston rings, to rubber components, to even tools used in assembly– all use DPM. This mark can take several forms dependent on the surface quality. DPM has methods for working with al kinds of surface – rough cast surfaces, machined surfaces, dust-covered surfaces, oil and grease covered surfaces etc. These marks are permanent and cannot fall off or fadeaway. Interestingly, the encoding system for DPM is the same as the one being currently used for RFID tags for Rolling Stock and major assemblies, such as, bogies. This is an internationally accepted standard by the governing body – GS1. As such, a smooth technological continuum currently exists that allows components along with the final assembly to be treated as one with a common data flow. So a bearing on an axle, fitted on some bogie, being used some coach can be tracked individually and as a whole at the same time. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 53 | H-Type Coupler Model to impart training of Coupling & Uncoupling |
Fully fledged working trolley of H-Type Coupler on track is prepared at DTTC-RTM to impart training to Running staff, Operating staff and shed maintenance staff. Railway Western Railway Subject Safety improvement Name of Good Work H-Type Coupler Model to impart training of Coupling & Uncoupling Summary Fully fledged working trolley of H-Type Coupler on track is prepared at DTTC-RTM to impart training to Running staff, Operating staff and shed maintenance staff. Detailed description Previously, repeated cases of Loco not coupling/uncoupling with load were happening at stations and yards due to lack of knowledge of Operating / Running staff and consequential detention of train / punctuality loss had been taking place. Moreover this problem had been creating a lot of inconvenience in those places like Chittaurgarh, Indore & Ratlam yard in Ratlam Division of WR, where RR has to be performed frequently to meet the operational requirements. Many times coupler lock pin got damaged and loco parted from train while starting. Since operation of H-Type Coupler is to be practically demonstrated to all the staff, there was limitation of time, place, duration and practical operation constraints in the yard and as such, training was not getting properly imparted. To overcome above issues and to ensure training of all the concerned through supervisors with physical demonstrations of all the subassemblies and procedure of assuring proper coupling, a fully fledged working trolley of H Type Coupler is made at DTTC, Ratlam (WR). Two H-type coupler one fixed to the structure and one moveable on trolley is placed on rail, has been developed. By moving trolley the operation / function of coupling, parts involved in coupling, proper coupling and decoupling operations etc. can be easily demonstrated to trainees. All the important aspects while performing H-type coupler operation like dropping of lock lifter, clearing of tell tale slot of rotary lock lift lever, vertical position of rotary lock lifter rib, parallelism of Knuckle & coupler head machined faces, proper fitment of lock pin of coupler etc. are demonstrated. With the introduction of training on this model, the knowledge of all the concerned staff has improved drastically which is helping in reducing the cases of decoupling in yards during attachments. Impact / Benefit Help to reduce MMBC & BWMS cases pertaining to H-type coupler significantly and thus enhanced the safety of train to avoid train parting and accident cases. Uploaded support documents/ Photographs/ Diagrams Contact Person Name Shri Vinod Kumar Contact Person Designation Sr. DME (DL)-RTM Contact Number +919752492450 |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54 | Reliability and Safety improvement |
CCB 1.5 Brake Valve testing bench is prepared in Quality Unit Air Brake of Diesel Shed Ratlam. After preparing this Test Bench all Pneumatic Brake Valve of CCB 1.5 system can be tested after the overhauling /necessary investigations after any line failure. Railway Western Railway Subject Reliability and Safety improvement Name of Good Work Test Bench for testing of CCB 1.5 Brake Valves. Summary CCB 1.5 Brake Valve testing bench is prepared in Quality Unit Air Brake of Diesel Shed Ratlam. After preparing this Test Bench all Pneumatic Brake Valve of CCB 1.5 system can be tested after the overhauling /necessary investigations after any line failure. Detailed Description Computer controlled brake system (CCB 1.5) designed by the M/s Knorr Bremse is a powerful braking system, which make it possible to apply as well as release the Loco & Train brakes quickly thus prevents time loss and also ensures safety during emergency application of the brakes. The system involves various Pneumatic as well as electrically operated complicated valves to run this brake system efficiently. Malfunctioning of any of the associated valves needs to be identified and rectified promptly to prevent detention of the loco in the shed. RTM shed had received its first CCB 1.5 Alco Loco in 2010. Presently there are 3 HHP Locomotives in shed which are having this type of brake system. CCB 1.5 brake System is having total 24 Brake Valves. M/s KBIL provides total 12 no. of Test Benches for the testing of all these Brakes valves. Each Test Bench is designed to test one or more than one types of valves only. RTM Diesel shed has made a single Test Bench to test 12 pneumatic valves of CCB 1.5 brake system. The total cost of M/s KBIL made Test Benches for testing of these 12 Valves are Rs.42 Lacs as per copy of a BQ available with us, whereas the shed has used available resources of Diesel Shed Ratlam to make this Test Bench. Many times brake valves are needed to be overhauled and tested in out of course/in schedule, but due to non-availability of testing facility, RTM shed has to test the culprit valves in OEM premises, which increases downtime of the concerned locomotives besides loss of man power of the shed. To overcome these entire issues, this Test Bench is made indigenously by available resources of Diesel Shed, Ratlam. As this Test Bench is made by scrap/condemn released material of Diesel Loco hence this Test Bench made by the RTM shed is not only a cost saver but also a very compact one, thus occupying lesser area on the shop floor. This will help to enhance the reliability of all 12 valves, those are supposed to be tested on this Test Bench. Impact/Benefit Helps to reduce BWMS cases pertaining to CCB 1.5 System Uploaded support documents / Photographs/Diagrams
Contact Person Name Shri Vinod Kumar Contact Person Designation Sr.DME(DL)-RTM Contact Number +919752492450 |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55 | Innovation/Good Work done in June - 2018 |
On the eve of World Environment day, Asansol Carriage & Wagon department unveiled a bio-toilet model & inaugurated by Mr. P.K. Mishra (Hon'ble DRM/ASN) under public awareness programme.
|
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 56 | Centre of Excellence Bogie and Shock Absorber Sections |
FIAT Bogie Shop - Centre of Excellence Cleaning of Bogies Click Here to view more information. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 57 | Prayas Book on LHB Pitline Maintenance |
Click here to view complete E-Book. |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 58 | Training Material प्रयास | PDF Open | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | Introduction to CTRB |
Introduction to CTRB |
PDF Open | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60 | How to use Wheel Distance Gauge on Indian Railway coaches ICF, LHB and Wagons |
How to use Wheel Distance Gauge Indian Railway coaches ICF LHB and Wagons |
PDF Open |














 A heavy duty hydraulic press has been developed by Sick line, SRC coaching depot which is very much useful to insert and extract different types of bushes like control arm, traction centre, traction rod, vertical roll link of LHB coaches, centre pivot push, anchor link bush of ICF/HYBRID coaches.
A heavy duty hydraulic press has been developed by Sick line, SRC coaching depot which is very much useful to insert and extract different types of bushes like control arm, traction centre, traction rod, vertical roll link of LHB coaches, centre pivot push, anchor link bush of ICF/HYBRID coaches.
 Thus the ML program “learns” about features that are unique to cats. When fed a new unclassified image, the ML program compares the features of the new image with the ones it has learned earlier and assigns the new image a classification based on its past “training”.
Thus the ML program “learns” about features that are unique to cats. When fed a new unclassified image, the ML program compares the features of the new image with the ones it has learned earlier and assigns the new image a classification based on its past “training”. Every component, part and critical asset can tell a story – of its manufacture, of its use, of its possible misuse. DPM is a technology that allows this story to be known – accurately and instantly. The medical screw on the right is used for joining broken bones. It has a squarish mark on the right side in the head – that is DPM at work. Each mark is unique to that piece anywhere across the world, Once marked, always marked, always known.
Every component, part and critical asset can tell a story – of its manufacture, of its use, of its possible misuse. DPM is a technology that allows this story to be known – accurately and instantly. The medical screw on the right is used for joining broken bones. It has a squarish mark on the right side in the head – that is DPM at work. Each mark is unique to that piece anywhere across the world, Once marked, always marked, always known.






